Literature Search & Review for MDR Compliance
A guide to medical device literature searches & reviews as critical components in effective MDR compliance strategies
What is a medical device literature search & review?
A systematic literature search & review is a structured and objective process which identifies, critically appraises and analyses clinical evidence in order to answer carefully formulated research questions.
It involves a thorough, methodical search of databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar to identify all literature sources relevant to the clinical background (SOTA) and/ or the subject device.
A systematic literature search & review should be performed in line with a search protocol, setting out the search terms to be used, inclusion/ exclusion criteria, appraisal framework, analysis criteria and justifications for decisions. It should also identify requirements for the qualifications of the individuals assigned to the review.
Literature search & review forms an important component of MDR compliance, forming key aspects of Clinical Evaluation, Risk Management and other parts of all effective MDR regulatory strategies.
What is the role of literature search & review in achieving MDR compliance?
Literature search & review is a pivotal component of the Clinical Evaluation of medical devices under the MDR. The importance of a systematic review of available evidence through this process is emphasised repeatedly in MedDev 2.7/1 rev 4 and is crucial in ensuring compliance with the new EU MDR.
1. Clinical Evaluation
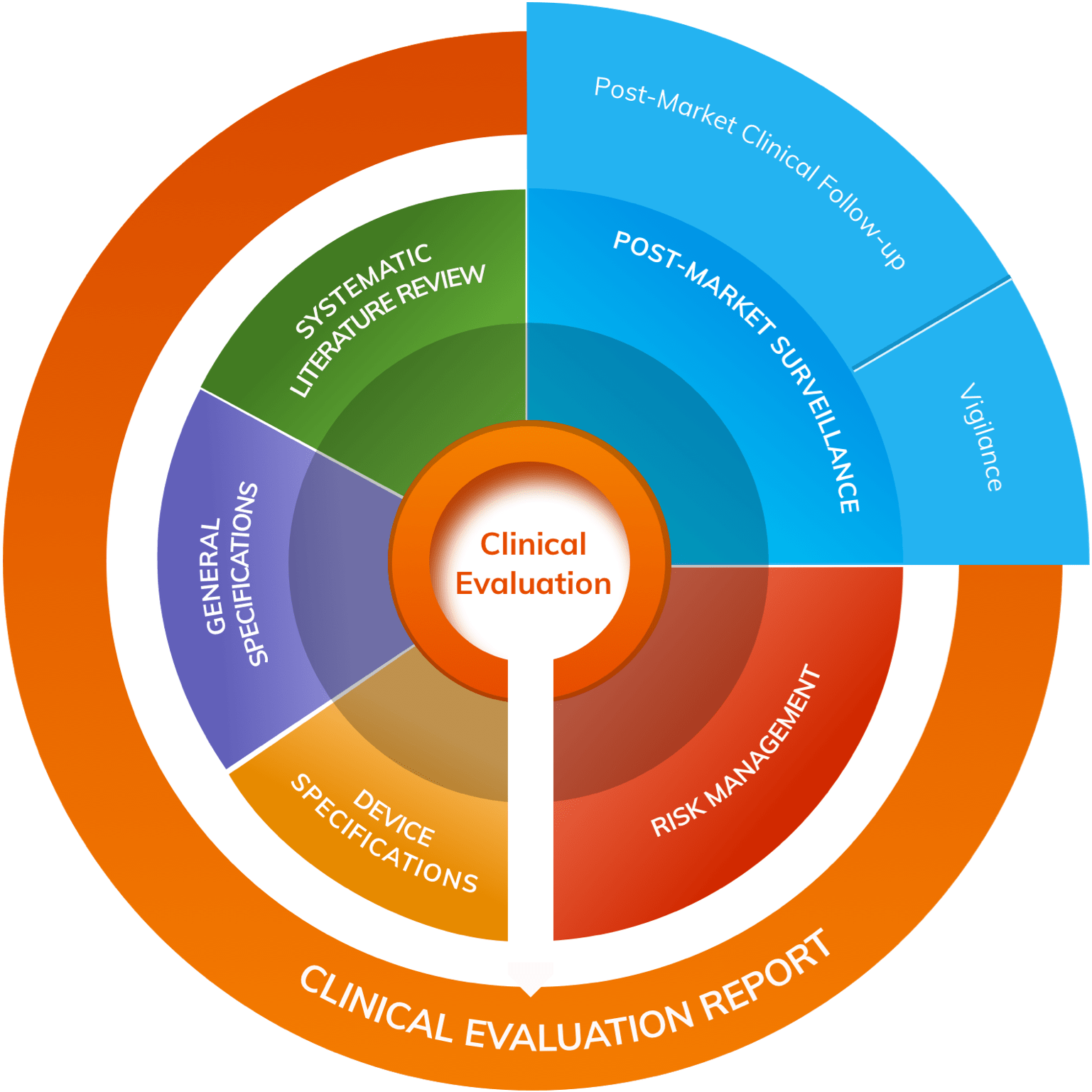
A literature search & review is a pivotal component of medical device Clinical Evaluation. According to MedDev 2.7/1 rev 4, they are essential for identifying safety and/or performance data relating to both the clinical background (State-of-the-Art) and to the subject device itself.
The Clinical Evaluation Plan (CEP) should set out a carefully designed literature search & review protocol to guide conduct of the evaluation and ensure that objective, rigorous standards are adhered to.
Effective literature searches are even more important in the event of a claim of equivalence, since the results of literature review on the equivalent device will stand in place of a clinical investigation of the device under consideration.
It can be expected that the methodology and conduct of the literature search & review will be intensely scrutinised by Clinical Evaluation Report reviewers, so ensure you have the right advice and the right approach to this crucial aspect of Clinical Evaluation.
2. PMS & PMCF
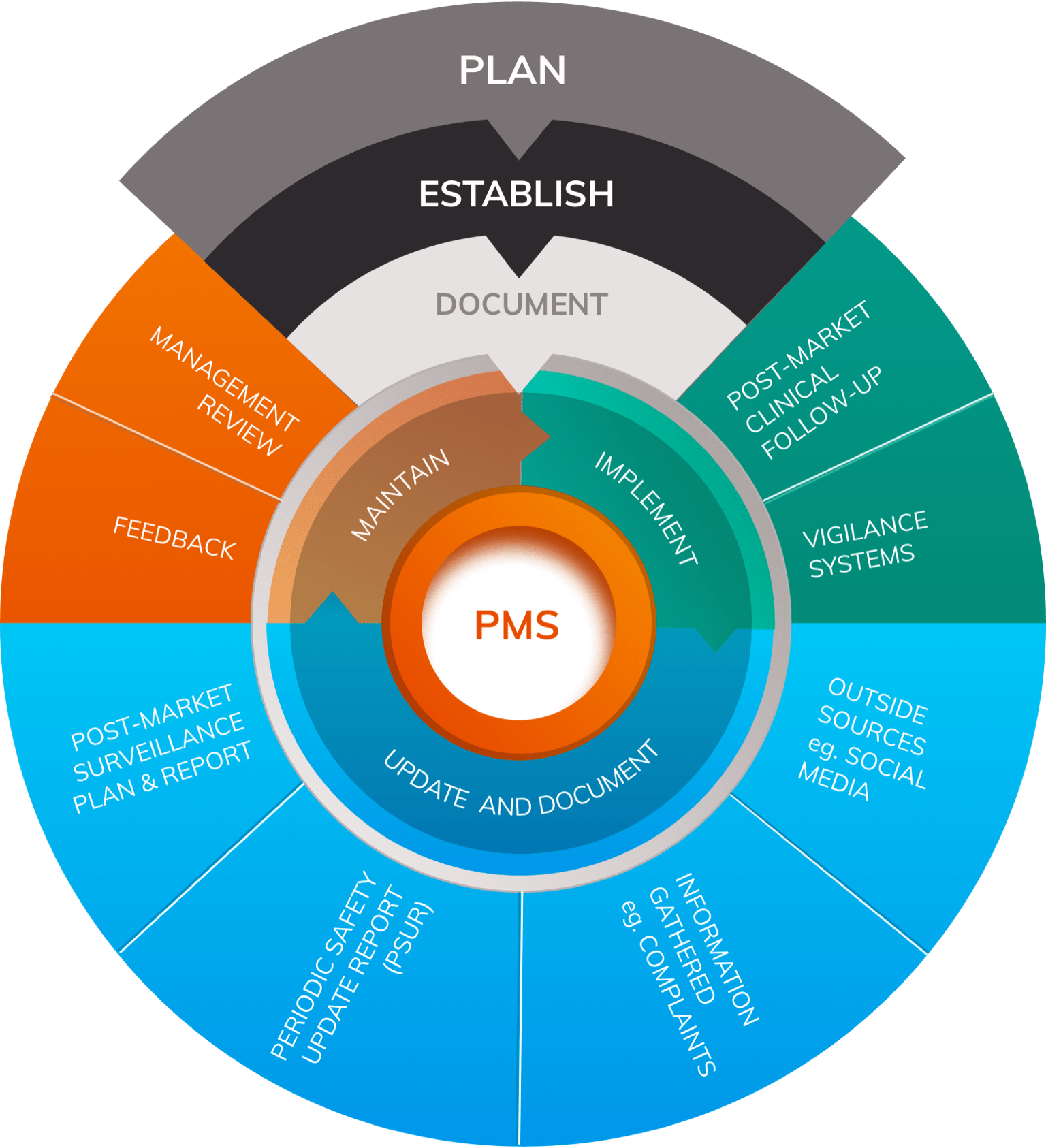
As part of the Quality Management System (QMS), manufacturers are expected to implement and maintain a Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) system that routinely evaluates the clinical performance and clinical safety of the device. The scope and nature of such PMS should correspond to the device and its intended use. PMS creates new data on a frequent basis (e.g. safety reports, results from published literature, registries, PMCF Studies, and other data about device usage). These data must be analysed for information that has the potential to alter the risk/benefit profile, as well as the clinical performance and clinical safety of the device.
Post-Market Clinical Follow-up (PMCF) activities should include scope for a regular, scheduled systematic review of the medical literature throughout the lifetime of a device; in turn, the results will inform the PMS Report/ PSUR, PMCF Report and the Clinical Evaluation Report (CER).
3. To establish State-of-the-Art (SOTA)
A systematic review of the literature is essential for identifying and analysing sources of clinical data relating to the clinical background and State-of-the-Art. As per MedDev 2.7/1 rev 4:
The State-of-the-Art embodies what is currently and generally accepted as good practice. The most technologically advanced solution is not always the State-of-the-Art.
According to the MedDev guidelines, a literature review should be used to describe the clinical background and identify current knowledge/ State-of-the-Art in the corresponding medical field of the subject device.
Consideration of evidence relating to comparable alternatives to the subject device should enable the determination of safety and performance benchmarks against which the subject device may be compared in the Clinical Evaluation.
The applicability of a State-of-the-Art review is not restricted to Clinical Evaluation – it can also be vital in competitor analysis, market analysis, and in identifying opportunities for product improvement or innovation.
4. Risk Management
A literature search of independently published evidence also forms a key input into the Risk Management process. It’s an essential step in identifying hazards (including hazards due to substances, technologies, and manufacturing procedures) and in producing evidence-based estimates of the probability and severity of risk.
Regular literature reviews can help ensure that Risk Management remains current and up to date. relating to subject device and/ or equivalent device can contribute to an effective Risk Management process.
An ongoing literature search & review enables proactive Risk Management by allowing organisations to identify and escalate concerns as they arise or before they become apparent, allowing them to take a proactive and dynamic approach to Risk Management.
How to structure the literature review
According to MedDev 2.7/1 rev 4, a literature review should include the following information:
- Introduction to the subject device
- Objectives/purpose of the literature review
- Search protocol which includes inclusion/ exclusion criteria and an appraisal & analysis plan
- Research questions that set out what you intend to discover from the literature review
- Search terms
- Analysis and appraisal of the literature identified
- Safety and performance benchmarks identified from the analysis
- List of exclusions and justification
Each component should be properly planned and prepared to ensure that the document is understandable by a reviewer who may not be familiar with the medical device.


